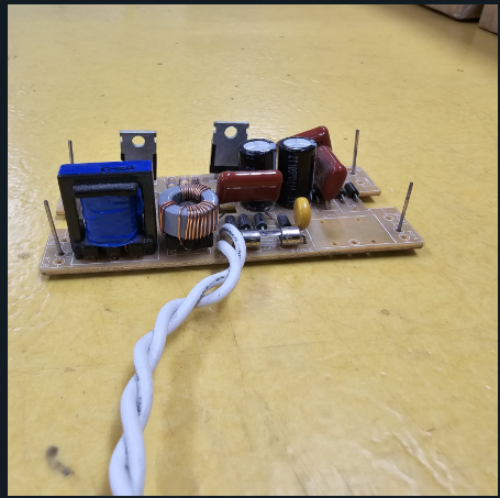
A transformer is an electrical device designed to modify the voltage level of alternating current (AC) in a circuit. It functions based on electromagnetic induction, utilizing two coils—primary and secondary—wound around a core. When an AC voltage is applied to the primary coil, it generates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil, thereby altering the voltage level. Depending on the turns ratio of the coils, a transformer can either step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the voltage. Transformers are essential for efficient electricity transmission and distribution, allowing high-voltage power to be transmitted over long distances and then reduced to safer, usable levels for homes and businesses.
Transformers are commonly used in power grids, industrial machinery, and a variety of electronic devices. Their efficiency and capability to operate over long distances make them vital components in electrical systems. Transformers come in different types based on their design and application, such as oil-cooled, air-cooled, and dry-type transformers. They can also be classified as single-phase or three-phase, each suited for different power needs. Their ability to adjust voltage without changing frequency makes transformers crucial for providing stable power to a wide range of applications.